When most people hear the words “brain injury,” they associate it with a concussion or head injury – which is usually called a Traumatic Brain Injury, or TBI. But brain injuries have a wide variety of causes, including non-traumatic brain injuries that damage the brain at the cellular level, and can be just as severe and debilitating. March is Brain Injury Awareness Month, and the traumatic brain injury lawyers at TorkLaw are observing it by sharing information about brain injury’s causes and effects, and the challenges of those living with brain injury.
 The Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA) has been raising public awareness of brain injuries and their effects for more than 30 years. Their current campaign is #ChangeYourMind, and its goal is to remove the stigma of brain injury through outreach, empowerment, and support for brain injury survivors and their caregivers.
The Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA) has been raising public awareness of brain injuries and their effects for more than 30 years. Their current campaign is #ChangeYourMind, and its goal is to remove the stigma of brain injury through outreach, empowerment, and support for brain injury survivors and their caregivers.
Here are some things you can do to support Brain Injury Awareness Month:
- Join the #ChangeYourMind Awareness Campaign.
- Download the #ChangeYourMind stamp.
- Share about Brain Injury Awareness Month on social media.
- If you are a brain injury survivor or caregiver, share your stories with others to help them understand what you’re going through.
- If you know a brain injury survivor or caregiver, reach out – they could probably use a helping hand or a sympathetic ear.
Types and Causes of Brain Injury
When a brain injury occurs after birth, it is sometimes called Acquired Brain Injury (ABI). This type of injury can be categorized in two primary types:
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
TBI is usually caused by an external force impacting the head, and causing the brain to move inside the skull. Most TBIs are concussions, or an injury that results in temporary loss of brain function, and they range from mild, in terms of a brief change in consciousness, or severe, resulting in an extended loss of consciousness, and damage and dysfunction to the brain. The effects of TBI can include permanent disabilities.
According to the Centers for Disease Control, each year, there are approximately 2.8 million traumatic brain injuries resulting in emergency department (ED) visits, hospitalizations and deaths. TBIs have many causes, but the most prevalent are falls, being struck by or against an object, motor vehicle accidents, and assault or abuse.
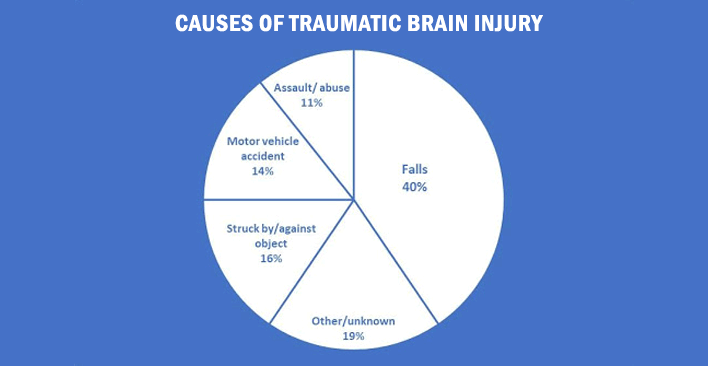
Source: https://www.biausa.org/public-affairs/public-awareness/campaigns/fact-sheet
These leading causes vary by age group:
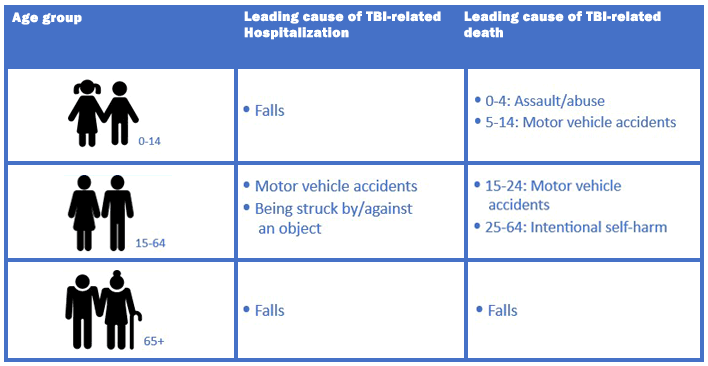
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/get_the_facts.htm
It should also be noted that military attack or bomb blast is also a major cause of TBI for those in the military: Since 2000, more than 383,000 U.S. service members have suffered a traumatic brain injury.
Non-Traumatic Brain Injury (NTBI)
Typically, NTBIs are categorized as anoxic or hypoxic brain injury types. These brain injuries occur due to a lack of oxygen to the brain: Anoxic brain injuries occur when the brain is completely cut off from oxygen, causing brain cells to die after about four minutes. Hypoxic brain injuries are those resulting from restricted levels of oxygen to the brain, causing gradual impairment or death of brain cells.
Causes of NTBI include:
|
|
Symptoms of Brain Injury
If you experience a bump or blow to your head, or to another part of your body, and you begin to have the following symptoms, it may indicate a blood clot pressing against your brain. Call 911 if you experience:
- A headache that keeps getting worse and doesn’t go away.
- Weakness or numbness in any part of your body.
- Dizziness or decreased coordination.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Speech difficulties.
If someone else has received a bump or blow to the head or body, and exhibits these signs, call 911 right away if they:
- Appear to be drowsy.
- Have a larger pupil in one eye than in the other.
- Experience convulsions or seizures.
- Are confused, or doesn’t know where they are or recognize people.
- Are unusually irritable, agitated or aggressive.
- Become unconsciousness.

Danger Signs in Children
If your child has fallen, hit his or her head, or suffered a blow to the head or body, call 911 right away if he or she:
- Exhibits any of the danger signs above.
- Doesn’t stop crying and seem inconsolable.
- Won’t nurse or eat.
Living with a Brain Injury
Many survivors of brain injury fully recover within a matter of weeks or months. However, many brain injury survivors may suffer lifelong effects to thinking, movement, or emotional functions. These problems are complex and impact survivors’ ability to work, perform basic self-care, and maintain relationships. This will not only affect the injured person, but caregivers and family members will need to learn to cope with these challenges.
Cognitive Effects
- Amnesia and memory issues: Short-term and “working memory” are often affected after brain injury; the injured person may have trouble remembering faces, names, conversations, or new information.
- Language: Brain injury may cause difficulty comprehending what is said or read, or in expressing the right words.
- Reasoning: Impairments to reasoning skills make it difficult for the person to think logically or organize information in their mind.
- Focus and concentration: Reduced attention span and problems completing tasks is a common problem for a brain injured person.
- Information processing: Brain-injured people may have problems making sense of what they see, hear or sense. For example, they may be unable to process the speed of oncoming traffic.

Physical Effects
- Mobility: Some survivors may need a wheelchair, walker, cane, or other mobility aids due to weakness or poor balance.
- Weakness and fatigue: Even mild brain injuries cause excessive fatigue; things that seem simple to the rest of us require much more energy and effort for a brain injury victim.
- Sensory impairment: Eyesight, hearing, smell, touch or taste may be reduced or lost.
- Epilepsy or ataxia: Brain-injured individuals may be prone to seizures or spastic, uncontrollable movements.
- Sexual dysfunction: Brain injured people may experiences changes in sexual desire, arousal, or performance. Desire/arousal may be significantly decreased, or may increase to the point of being uncontrolled.
Emotional Effects
- Depression and anxiety: Depression, a sense of loss, and anxiety about the future are common for any injury; for those with brain injuries, it may be even harder to deal with these feelings.
- Reduced empathy: Impaired insight or self-awareness may make it difficult for the brain-injured person to understand situations from another’s perspective; they may become unaware of the effect their behavior has on others.
- Irritability, aggression: People with brain injuries often become impatient and easily irritated by others; they may be easily frustrated or short-tempered.
- Disinhibition and impulsiveness: A brain-injured person may become unaware of what is appropriate and may make rude remarks or use bad language; they may speak and act without thinking.
- Obsessiveness: A person may become fixated on certain thoughts or actions after a brain injury.
Treatment
A neurologist will determine the extent and effect of brain damage, and prescribe treatment to prevent further injury; for instance, medication to control blood pressure or ensure the brain is receiving enough blood and oxygen. Additionally, most brain-injured patients benefit from rehabilitative therapy such as physical and occupational therapy, speech and language therapy, as well as psychological support and counseling.
Treatment and care of brain injuries has a high financial, physical, and emotional cost to victims and their families. Anyone who has received brain injuries at the hands of another should contact a law firm experienced in brain injury law to seek compensation to help cover medical treatment, rehabilitative treatment, long-term care, ancillary care, and pain and suffering.
Prevention
Most brain injuries can be prevented. Here are some ways to reduce your risk of brain damage and spinal cord injury:
- Wear your seatbelt and drive carefully.
- Never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Always wear a helmet during sports or cycling.
- Use handrails on stairways, and step stools to reach high objects.
- If you have guns, keep them unloaded and locked in a proper gun safe or cabinet.
If you or a loved one has suffered a brain injury through no fault of your own, you may be entitled to significant compensation, whether your injury occurred as a result of a car accident, a fall on someone else’s property, a defective sports helmet, or even assault. If you have not received an appropriate amount to help you deal with the difficult and long-term effects of brain injury, give the experienced brain injury attorneys at TorkLaw a call – we have successfully represented hundreds of brain injury cases, and we can help you. Contact us today at 888.845.9696.
Did you find this post informative? You may also want to check out the below content: